ROBOT NAVIGATION - TD3 ALGORITHM
Advanced Robot Navigation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning

Year
2023
Author
Mohamed Ifqir
Framework
ROS Noetic, PyTorch
Project
Robot Navigation with TD3
Programming Languages
Python, C++, C, Shell
Algorithm
TD3 (Twin Delayed DDPG)
Github
Robot Navigation
App link
Not available
Description
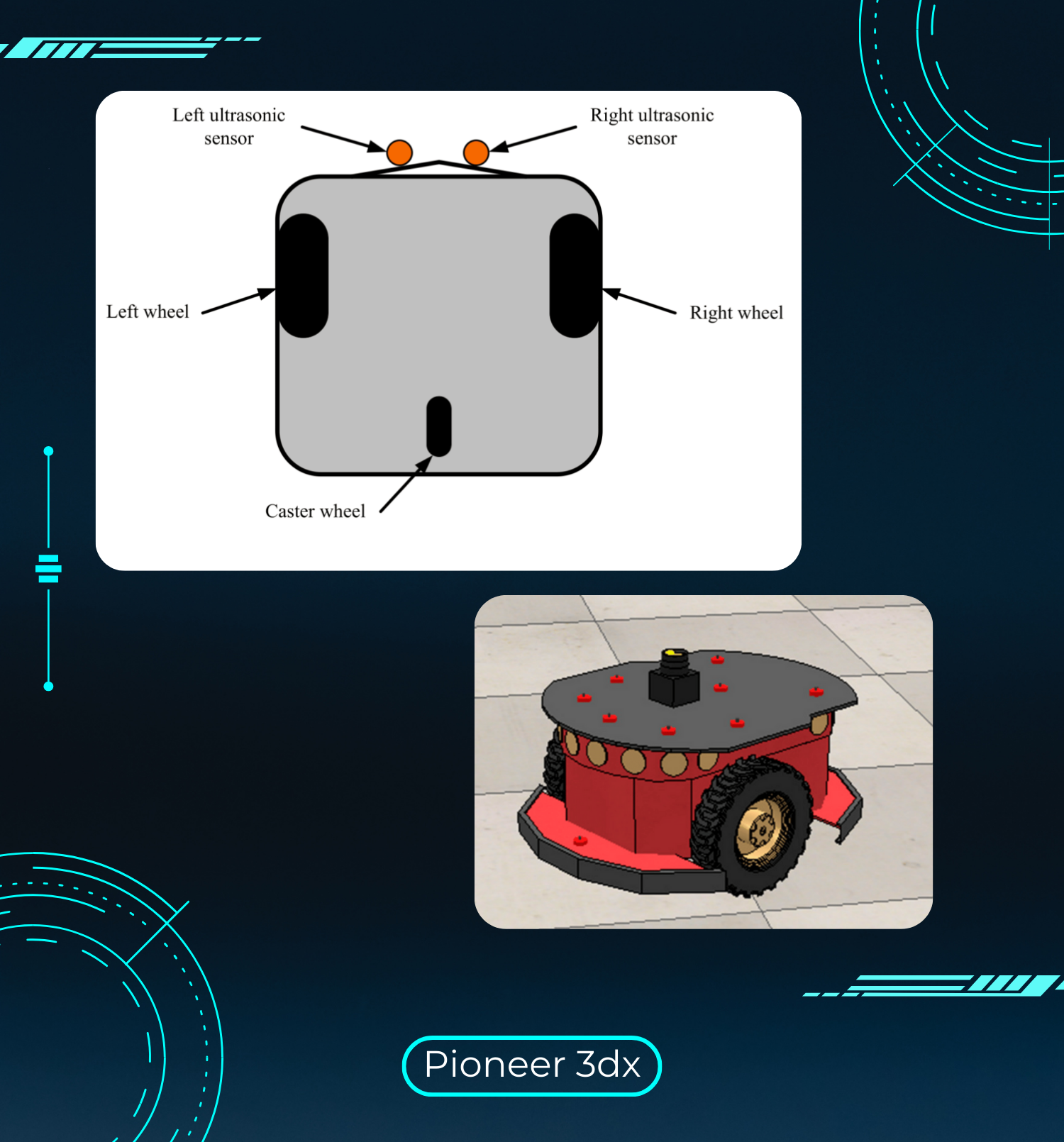
This project leverages the TD3 (Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient) algorithm to enhance robot navigation capabilities within a simulation environment using ROS Noetic, Gazebo, and RViz. The TD3 algorithm, a variant of DDPG (Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient), addresses common stability issues in reinforcement learning by introducing twin critics and delayed policy updates. This structure significantly enhances learning stability and efficiency, especially in complex environments.
With PyTorch as the backbone for training and deploying the reinforcement learning model, this project incorporates ROS for real-time robot control, enabling seamless navigation through continuous updates and feedback. Gazebo serves as the 3D simulation environment, while RViz is used for visualizing robot states, paths, and sensor data. This setup provides a comprehensive platform for testing and refining the robot's navigation skills.
TD3 Algorithm for Robot Navigation
- Actor-Critic Architecture: Uses two critics (Q-networks) to reduce overestimation bias and one actor (policy network) for optimal action selection based on current state observations.
- Twin Critic Networks: Computes two Q-values for each action and uses the minimum value to stabilize training and avoid overly optimistic estimates.
- Delayed Policy Update: The actor network updates less frequently than the critics, allowing more stable policy changes and reducing feedback noise.
- Target Policy Smoothing: Adds noise to target actions to make the policy less sensitive to minor variations, helping to prevent erratic behaviors during navigation.
- Experience Replay: Stores and samples past experiences to improve data efficiency and enhance model robustness across various navigation scenarios.
- Continuous State and Action Space: Facilitates smooth, real-time control by working in a continuous action space, which is essential for precise robotic motion control.
Are You Ready to kickstart your project with a touch of magic and a whole lot of coding?
Reach out and let's make it happen ✨. I'm also available for full-time or Part-time opportunities to push the boundaries of Machine learning and AI.